Indian Accounting Standards Series: Fair Value Recognition
As we last saw, revenue recognition reporting could bring about adverse company financials. We mark upon our journey to understand a few more accounting standards to better understand our investments. Assets and Liabilities are recognized on the balance sheet with different measurement techniques which could also give rise to material differences. On the balance sheet of the company, the assets and liabilities are commonly reported at cost value which could be a divergence from economic reality as the current market value of these assets could be lower or higher. Thus fair value accounting takes into consideration the current values of assets and liabilities at which one could sell them in the market. Although companies still have the option to choose between fair value or cost method for physical assets valuation. For financial assets valuation, the Fair value method is used.
The accounting is different for Physical assets and financial assets.
Physical Assets like property, plant and equipment: If the companies choose the option of revaluing groups/blocks of assets at fair value instead of the cost model then revaluation reserves will be created and the net worth of the company will increase. The depreciation charge for the remaining useful life of the asset will increase. This can reduce future profits.
For Financial instruments: Under this, the companies have the option to value financial assets such as equity shares at Fair Value Through P&L (Profit & loss) (FVTPL) or Fair Value Through Comprehensive Income (FVTOCI). FVTPL is chosen when shares are held for trading purposes, which simply means that the shares are bought for the mere scope of selling them at a profit. Trading securities are usually short-term or have a determined period of holding. FVTOCI is chosen when shares are held for trading as well as collecting the cash flows over the investment period.
Cashflows of investments generally include interest received, coupons received, buybacks, dividends etc. When the company is interested in earning cash flows and holding the security for the long term it would report it through Other Comprehensive Income (OCI).
Classification for financial asset is based on :
-
The entity’s business model for managing the financial assets.
-
The contractual cash flows characteristics of the financial asset.
Material Effect:
When shares are reported at Fair value through P&L, the profit or loss on this security would be reflected on the company’s statement of profit and loss. Thus, the company’s intent is to hold the investment for trading purposes or to gain some returns.
When shares are reported at Fair Value through other comprehensive income methods, then the company’s intent is to gain cash flows from dividends or interest and also be held for trading. The profit/loss under this statement would directly be reflected on the company’s reserves. The option to choose FVTPL OR FVTOCI is based on the intent/ purpose of holding the asset.

Eg1: Info Edge Limited holds investments in companies like Zomato Ltd and PB Fintech. It has chosen to value these investments at fair value through OCI (Other comprehensive income) at each quarter end. It means that the profit or loss on marking the value to market will be reflected in the reserves of the company. As Info Edge has chosen to value them at FVOCI i.e. with a view that these are held for trading purposes as well as to collect the contractual cash flows. Otherwise, if they were held only for trading, profits or gains would have been recognized in Profit after tax (PAT). And the PAT figure would have been volatile.

Eg2: Here Nippon AMC intends to earn returns on surplus cash generated from operations and thus the focus is on overall returns, not specific investments. It does not have the intention to collect cash flows from the specific investments made. Hence it has classified the investments as FVTPL.
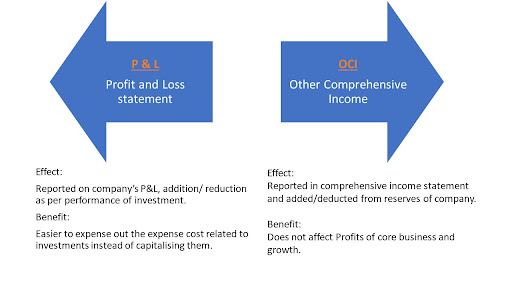
Investor perspective: In the above example we saw that a company recognizing a particular asset through P&L or OCI makes a great material difference to analyze the performance of the company.
FVTPL
- FVTPL can make the PAT (Profit after tax) volatile and uncertain depending on the mark-to-market charges.
- FVTPL requires the profit/loss to be charged in P&L.
- Core business margins may not show the correct picture from an investor’s perspective and it may be difficult to forecast the earnings trajectory of the company if mark to market charge is significant.
- This option is chosen by companies when they invest surplus cash balances and are interested in overall returns rather than individual assets in the portfolio.
FVOCI
- FVOCI keeps investment gain/loss separate from the core business, as it is reported in the OCI which is presented below PAT and further routed directly to reserves.
- FVOCI adds/ deducts from reserves of the company and hence the analysis of a core business is relatively easier.
- FVOCI can aid to capitalize on the expenses related to investments like broking, transaction cost, etc.
- When companies are interested in individual investments and their cash flows, they may make an irrevocable election to classify investments as FVTOCI.
Conclusion:
Understanding the reporting of assets/ investments of companies is vital to understanding their effect on the company’s core business. The material effect of financials can be on cash flows, debt & solvency ratios, etc. This analysis is important as one may get misguided and take uninformed decisions about a company’s performance. Equity research is not merely to study the company numbers but to make meaning out of them. Stay tuned for our next blog on similar accounting standards which will make you a smart investor.
AUTHOR: Noopur Patil





